In the realm of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, Cupric Chloride Etchant stands as a powerful ally in achieving precision and control during the wet etching process. This chemical solution, composed of cupric chloride (CuCl2), enables engineers to selectively remove copper from PCB substrates, shaping intricate circuit patterns. In this blog, we will delve into the specifics of Cupric Chloride Etchant and provide valuable tips for its effective utilization in PCB wet etching machines.
What is Cupric Chloride Etchant?
Cupric Chloride Etchant is an acidic solution containing cupric chloride, a chemical compound known for its ability to dissolve copper efficiently. This etchant is widely used in the PCB manufacturing industry for its excellent selectivity, allowing for precise copper removal without adversely affecting other materials on the PCB.
Tips for Using Cupric Chloride Etchant in PCB Wet Etching Machine:
- Etchant Preparation:
To prepare the Cupric Chloride Etchant solution, mix cupric chloride crystals with hydrochloric acid (HCl) in a proper ratio. The common ratio is approximately 100 grams of cupric chloride per 100 milliliters of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Always add the acid to the water slowly while stirring, and ensure you’re working in a well-ventilated area with proper safety equipment.
- Temperature Control:
Maintaining the right temperature is crucial for achieving accurate etching results. The ideal operating temperature for Cupric Chloride Etchant typically ranges from 35°C to 50°C (95°F to 122°F). Consider using a temperature-controlled wet etching machine to ensure precise regulation.
- Immersion Time:
The etching time is directly related to the depth of copper removal. Longer immersion times result in deeper etching, while shorter times yield shallower patterns. The immersion time can vary depending on the desired circuit design and the thickness of the copper layer.
- Agitation:
Gentle agitation of the etchant solution can enhance the etching process by promoting even distribution. Proper agitation helps prevent over-etching or under-etching and ensures uniformity across the PCB surface.
- Neutralization and Disposal:
After the etching process, neutralize the Cupric Chloride Etchant to ensure it is deactivated and rendered safe for disposal. Utilize a neutralizing agent, such as sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), to neutralize the etchant solution before disposing of it responsibly according to environmental regulations.
- Safety Precautions:
Cupric Chloride Etchant is corrosive and toxic, requiring careful handling. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), work in a well-ventilated area, and follow proper safety protocols to avoid accidents and exposure to harmful fumes.
About Cupric and Alkaline
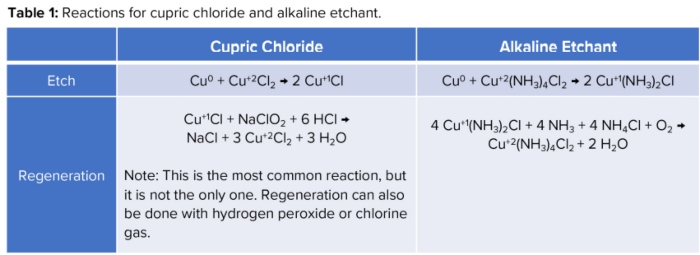
Together, these etchants are used in the majority of PCB etch shops, with alkaline being the most popular. To provide a baseline of how they work, their etch reactions along with their corresponding regeneration reactions, can be found in Table 1.
One of the main reasons these two etchants are the most used is because of their regeneration capabilities. With regeneration, you increase the capacity of copper you can etch. It also helps keep the etch rate at a consistent value. To maintain mass production of PCBs, it is important to keep the etch rate steady but also high enough to maximize output. Since etch rate can greatly influence production rates, it is a major factor when comparing etchants.
https://pcb.iconnect007.com/index.php/article/132406/the-chemical-connection-etchants-of-the-industrycupric-vs-alkaline/132409/?skin=pcb
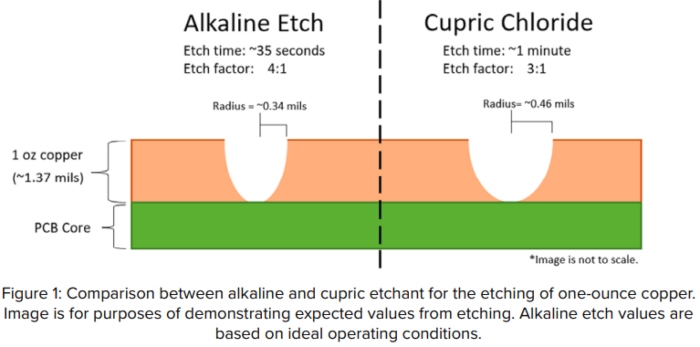
Etch Factor
Another matter where alkaline etchant is highly favored is etch factor, the ratio of downward etch to sideways etch. Alkaline etchant offers the benefit of a 4-to-1 etch factor (meaning it etches downward four times as much as it etches sideways). Cupric provides a standard 3-to-1 etch factor (Figure 1).

Alkaline etchant’s better etch factor opens the opportunity to maintain finer spaces and line widths when you are etching panels with thicker copper layers. Although alkaline can provide a great etch factor, a 4-to-1 ratio can only be obtained if the etchant is kept at its optimal condition, which is easier said than done.
Mastering the art of Cupric Chloride Etchant in PCB wet etching opens the door to unparalleled precision and control in circuit pattern creation. By adhering to proper etchant preparation, temperature regulation, immersion time, and safety precautions, engineers can craft intricate PCB designs with confidence. Embrace the power of Cupric Chloride Etchant and elevate your PCB manufacturing process to new heights of accuracy and efficiency.
In the realm of printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, Cupric Chloride Etchant stands as a powerful ally in achieving precision and control during the wet etching process. This chemical solution, composed of cupric chloride (CuCl2), enables engineers to selectively remove copper from PCB substrates, shaping intricate circuit patterns. In this blog, we will delve into the specifics of Cupric Chloride Etchant and provide valuable tips for its effective utilization in PCB wet etching machines.

