Standard RF shields are a critical component in the design of electronic devices, providing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) protection to sensitive components. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of standard RF shields, their benefits, and their applications.
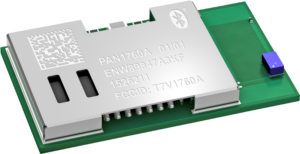 RF shields are designed to block or limit the flow of electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, ensuring that electronic devices operate smoothly without interference. Standard RF shields are typically made of a conductive material such as copper, silver, or aluminum, and are shaped to fit over electronic components or entire devices.
One of the primary benefits of standard RF shields is their ability to provide EMI and RFI protection. Without this protection, electronic devices can experience signal interference, leading to poor performance or even failure. Standard RF shields work by reflecting or absorbing electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, preventing them from interfering with sensitive components.
Another benefit of standard RF shields is their ease of use. RF shields are typically designed to fit over specific electronic components or devices, making installation straightforward and hassle-free. Additionally, many standard RF shields are reusable, allowing them to be removed and reinstalled as needed.
Modern precision sheet metal fabrication includes a common technique known as etching, which differs from traditional sheet metal fabrication in several ways. Here are some key differences between etching and traditional precision sheet metal fabrication:
RF shields are designed to block or limit the flow of electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, ensuring that electronic devices operate smoothly without interference. Standard RF shields are typically made of a conductive material such as copper, silver, or aluminum, and are shaped to fit over electronic components or entire devices.
One of the primary benefits of standard RF shields is their ability to provide EMI and RFI protection. Without this protection, electronic devices can experience signal interference, leading to poor performance or even failure. Standard RF shields work by reflecting or absorbing electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, preventing them from interfering with sensitive components.
Another benefit of standard RF shields is their ease of use. RF shields are typically designed to fit over specific electronic components or devices, making installation straightforward and hassle-free. Additionally, many standard RF shields are reusable, allowing them to be removed and reinstalled as needed.
Modern precision sheet metal fabrication includes a common technique known as etching, which differs from traditional sheet metal fabrication in several ways. Here are some key differences between etching and traditional precision sheet metal fabrication:
 RF shields are designed to block or limit the flow of electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, ensuring that electronic devices operate smoothly without interference. Standard RF shields are typically made of a conductive material such as copper, silver, or aluminum, and are shaped to fit over electronic components or entire devices.
One of the primary benefits of standard RF shields is their ability to provide EMI and RFI protection. Without this protection, electronic devices can experience signal interference, leading to poor performance or even failure. Standard RF shields work by reflecting or absorbing electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, preventing them from interfering with sensitive components.
Another benefit of standard RF shields is their ease of use. RF shields are typically designed to fit over specific electronic components or devices, making installation straightforward and hassle-free. Additionally, many standard RF shields are reusable, allowing them to be removed and reinstalled as needed.
RF shields are designed to block or limit the flow of electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, ensuring that electronic devices operate smoothly without interference. Standard RF shields are typically made of a conductive material such as copper, silver, or aluminum, and are shaped to fit over electronic components or entire devices.
One of the primary benefits of standard RF shields is their ability to provide EMI and RFI protection. Without this protection, electronic devices can experience signal interference, leading to poor performance or even failure. Standard RF shields work by reflecting or absorbing electromagnetic waves and radio frequency signals, preventing them from interfering with sensitive components.
Another benefit of standard RF shields is their ease of use. RF shields are typically designed to fit over specific electronic components or devices, making installation straightforward and hassle-free. Additionally, many standard RF shields are reusable, allowing them to be removed and reinstalled as needed.
Difference between traditional sheet metal precision processing VS Chemical etched sheet metal processing
VECO’s video to learn what metal etching is.
Comments related to etching technology:
From @chadr2604: There is another way it involves stacking many layers of very thin material with an There is another way it involves stacking many layers of very thin material with an adhesive, pressing the stack, then either stamping or punching the blank then heating it to release the adhesive. The parts will not be as accurate the tolerance is limited to about .002″ but if its good enough its much faster.
From @chadr2604: If you try to cut that stack with a laser you will just start a fire we had an aluminum fire trying that.
-
- Principle: Traditional sheet metal fabrication typically involves mechanical processes such as cutting, bending, and punching to shape and form metal sheets. Metal etching by Metal Etching Machine , on the other hand, is a chemical process that uses specialized etchants to selectively corrode the metal surface, achieving precise etched patterns and features.
- Accuracy and Complexity: Etching offers advantages in terms of precision and complexity. By controlling the composition, concentration, temperature, and etching time of the etchant, extremely fine etching can be achieved with accuracy down to sub-micron levels. Additionally, etching allows for the creation of intricate geometries, microstructures, and patterns that may be difficult to achieve using traditional mechanical methods.
- Processing Speed and Cost: Etching generally offers faster processing speeds, particularly in large-scale production. In comparison, traditional mechanical fabrication methods may require more time and cost to achieve the same level of precision and complexity.
- Materials Compatibility: Etching techniques are applicable to a range of metal materials, such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. Traditional sheet metal fabrication methods may have limitations when it comes to certain materials or thicker metal sheets.
- Design Flexibility: Etching provides greater design flexibility. By incorporating techniques like photolithography or screen printing during the etching process, complex patterns and structural designs can be achieved. This makes etching suitable for applications in microelectronics, optical devices, microfluidic devices, and more.
- Cellular phones and other wireless devices: Standard RF shields are used to protect sensitive components and reduce signal interference in cellular phones and other wireless devices.
- Aerospace and defense: Standard RF shields are used to protect avionics and other sensitive electronic components from interference in aircraft and spacecraft.
- Medical devices: Standard RF shields are used to protect medical devices such as pacemakers and implantable defibrillators from electromagnetic interference.
- Automotive: Standard RF shields are used to protect electronic components in vehicles from EMI and RFI, ensuring that the systems operate smoothly and reliably.
-
- Principle: Traditional sheet metal fabrication typically involves mechanical processes such as cutting, bending, and punching to shape and form metal sheets. Metal etching by Metal Etching Machine , on the other hand, is a chemical process that uses specialized etchants to selectively corrode the metal surface, achieving precise etched patterns and features.
- Accuracy and Complexity: Etching offers advantages in terms of precision and complexity. By controlling the composition, concentration, temperature, and etching time of the etchant, extremely fine etching can be achieved with accuracy down to sub-micron levels. Additionally, etching allows for the creation of intricate geometries, microstructures, and patterns that may be difficult to achieve using traditional mechanical methods.
- Processing Speed and Cost: Etching generally offers faster processing speeds, particularly in large-scale production. In comparison, traditional mechanical fabrication methods may require more time and cost to achieve the same level of precision and complexity.
- Materials Compatibility: Etching techniques are applicable to a range of metal materials, such as copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. Traditional sheet metal fabrication methods may have limitations when it comes to certain materials or thicker metal sheets.
- Design Flexibility: Etching provides greater design flexibility. By incorporating techniques like photolithography or screen printing during the etching process, complex patterns and structural designs can be achieved. This makes etching suitable for applications in microelectronics, optical devices, microfluidic devices, and more.
- Cellular phones and other wireless devices: Standard RF shields are used to protect sensitive components and reduce signal interference in cellular phones and other wireless devices.
- Aerospace and defense: Standard RF shields are used to protect avionics and other sensitive electronic components from interference in aircraft and spacecraft.
- Medical devices: Standard RF shields are used to protect medical devices such as pacemakers and implantable defibrillators from electromagnetic interference.
- Automotive: Standard RF shields are used to protect electronic components in vehicles from EMI and RFI, ensuring that the systems operate smoothly and reliably.
