
- PCB etching process video
- Introduction to Etching Machines
- Advantages of Using Etching Machines
- Factors you need to consider when buying an etching machine
- Automation and Efficiency
Precision and Accuracy - Chemical Compatibility and Safety
- Maintenance and Support
- Etching Machine Types
Popular Wet Processing Equipment for PCB
- metal etching process video
When you submit your requirements, we will give you advice within 2 days.
PCB Etching
Advantages
Purchasing factors
Machine Types
Etching machine brand
PCB Etching
Understanding the Importance of Etching Machines
A video to let you know the working process of PCB etching
Wet Processing Equipment for PCB
1.1 Introduction to Etching Machines
Before diving into the selection process, it’s crucial to understand what an etching machine is and why it plays a vital role in PCB manufacturing. An etching machine is a specialized device used to remove unwanted copper from the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) to create circuit traces. It employs chemical processes to selectively dissolve the copper, leaving behind the desired circuitry pattern. Etching machines are an integral part of the PCB production process, enabling the creation of intricate and precise circuit designs.
Learn about pcb etching through video
Advantages
1.2 Advantages of Using Etching Machines
Highlight the benefits of utilizing etching machines, such as increased efficiency, improved precision, reduced production time, and cost savings. Emphasize how these advantages can directly impact the success and profitability of your PCB manufacturing business. Some key advantages to consider:
-
- Increased Efficiency: Etching machines automate the intricate and time-consuming process of removing copper from PCBs. They can handle large volumes of boards in a shorter time, significantly increasing production efficiency.
-
- Improved Precision: Etching machines offer high accuracy and repeatability, ensuring consistent results and minimizing errors. They can achieve fine circuit traces and complex designs that may be challenging to accomplish manually.
-
- Reduced Production Time: With faster etching speeds and automated processes, etching machines can significantly reduce the overall production time, enabling quicker turnaround for PCB orders.
-
- Cost Savings: By minimizing manual labor and reducing material waste, etching machines can lead to cost savings in the PCB manufacturing process. Additionally, the increased efficiency and reduced production time can help optimize resource utilization and improve profitability.
Purchasing factors
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Etching Machine
2.1 Production Requirements
Discuss the importance of evaluating your specific production requirements, including the expected workload, desired production volume, and types of PCBs you plan to manufacture. This analysis will help you determine the ideal size and capacity of the etching machine needed. Consider the following factors:
-
- Workload: Assess the number of PCBs you intend to produce within a given timeframe. This will help determine the throughput and capacity requirements of the etching machine.
-
- Production Volume: Consider the quantity of PCBs needed for each production run. This will help determine whether a batch or continuous etching machine is more suitable for your needs.
-
- PCB Types: Evaluate the complexity and size of the PCBs you plan to manufacture. Some etching machines may be better suited for specific board sizes or designs.
2.2 Automation and Efficiency
Explain the significance of automation features in an etching machine. Discuss how automated processes can enhance efficiency, reduce human error, and increase productivity. Highlight key automation features to look for when choosing an etching machine, such as:
-
- Automatic Loading and Unloading: Machines equipped with automatic loading and unloading capabilities streamline the production process by reducing manual handling and setup time.
-
- Conveyor Systems: Etching machines with conveyor systems enable continuous processing of PCBs, allowing for higher throughput and minimizing downtime between batches.
-
- Software Integration: Look for machines that offer software integration for seamless control and monitoring of the etching process. This can enhance process visibility, data logging, and analysis.
2.3 Precision and Accuracy
Delve into the importance of precision and accuracy in PCB manufacturing. Explain how the quality of the etching machine’s components, such as the etching nozzle and positioning system, can impact the accuracy of the etching process. Discuss the significance of high-resolution imaging systems and advanced control algorithms in achieving precise and accurate results.
-
- Etching Nozzle: The quality and design of the etching nozzle play a crucial role in achieving precise and uniform etching. Look for machines that offer high-quality nozzles and ensure uniform distribution of etching solution.
-
- Positioning System: A robust and accurate positioning system is essential for maintaining the required alignment between the PCB and the etching solution. Consider machines with advanced positioning systems that offer precise control and alignment capabilities.
-
- Imaging Systems: High-resolution imaging systems can assist in accurate alignment and provide real-time feedback on the etching process. Look for machines that incorporate imaging technology to enhance precision and ensure optimal results.
-
- Control Algorithms: Advanced control algorithms can help optimize the etching process by adjusting parameters based on real-time data and feedback. Machines with intelligent control systems can improve accuracy and minimize errors.
2.4 Chemical Compatibility and Safety
Address the need to consider the compatibility of the etching machine with the chemicals used in the etching process. Discuss safety features, such as fume extraction systems and chemical waste management, that ensure a safe working environment and compliance with regulations.
-
- Chemical Compatibility: Verify that the materials used in the construction of the etching machine are compatible with the chemicals employed in the etching process. Chemical resistance is crucial to ensure the longevity of the machine.
-
- Fume Extraction Systems: Etching processes often generate fumes that can be hazardous to health. Look for machines that incorporate efficient fume extraction systems to remove and filter these fumes, providing a safe working environment.
-
- Chemical Waste Management: Etching processes generate chemical waste that must be handled and disposed of properly. Consider machines that offer adequate waste management features, such as collection and treatment systems, to comply with environmental regulations.
2.5 Maintenance and Support
Highlight the significance of considering the maintenance requirements and availability of technical support for the chosen etching machine. Discuss the importance of regular maintenance to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of the machine. Mention the value of prompt and reliable technical support for troubleshooting and repairs.
-
- Maintenance Requirements: Understand the recommended maintenance procedures and frequency for the etching machine. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, calibration, and component replacement, is vital for maximizing the machine’s lifespan and performance.
-
- Technical Support: Ensure that the manufacturer or supplier offers reliable technical support for the etching machine. Prompt assistance for troubleshooting, repairs, and spare parts availability can minimize downtime and ensure uninterrupted production.
Machine Types
Exploring Etching Machine Types
3.1 Spray Etching Machine
Provide an overview of spray etching machines, their operation principles, and the advantages they offer. Discuss their suitability for specific PCB manufacturing requirements and mention any limitations or considerations.
-
- Operation Principles: Spray etching machines employ nozzles to spray etching solution onto the PCB surface. The solution selectively dissolves the exposed copper, resulting in circuit pattern formation.
-
- Advantages: Spray etching machines offer versatility and are suitable for various PCB designs. They can handle both small and large board sizes efficiently. They are generally faster than dip etching machines and can achieve high-quality results.
-
- Limitations: Spray etching may not be suitable for boards with complex or fine-pitch designs, as the etching solution may not reach narrow spaces effectively.
3.2 Dip Etching Machine
Discuss dip etching machines, their operation, and how they differ from spray etching machines. Highlight their advantages, limitations, and suitable applications.
-
- Operation Principles: Dip etching machines immerse the PCBs in a tank filled with etching solution. The solution dissolves the exposed copper, leaving behind the desired circuitry.
-
- Advantages: Dip etching machines are well-suited for complex and fine-pitch designs, as the etching solution can reach narrow spaces effectively. They also provide uniform etching across the entire board.
-
- Limitations: Dip etching machines may have slower etching speeds compared to spray etching machines. They require careful control of immersion time and solution agitation to ensure consistent results.
3.3 Hybrid Etching Machine
Introduce hybrid etching machines that combine the capabilities of both spray and dip etching machines. Explain how they can offer flexibility and versatility in the etching process, allowing for different PCB designs and requirements. Hybrid machines provide the benefits of both spray and dip etching, enabling efficient processing of a wide range of PCB designs.
Etching machine brand
Top Etching Machine Brand
Popular Wet Processing Equipment for PCB
4.1 Dragon Etching Machine
Precision: The etching precision of our machine is 0.018mm, which allows us to manufacture micro-sized components with high accuracy.
Speed: The etching speed of our machine is determined by the quality and temperature of the etching solution used. Typically, higher temperatures result in faster etching.
Yield: Our machine achieves a high yield rate of 99.9% due to its high precision and controllable etching speed, which greatly improves manufacturing efficiency and reduces costs.
Manpower: Only two employees are needed to operate and maintain each machine, which reduces labor costs and increases production efficiency.
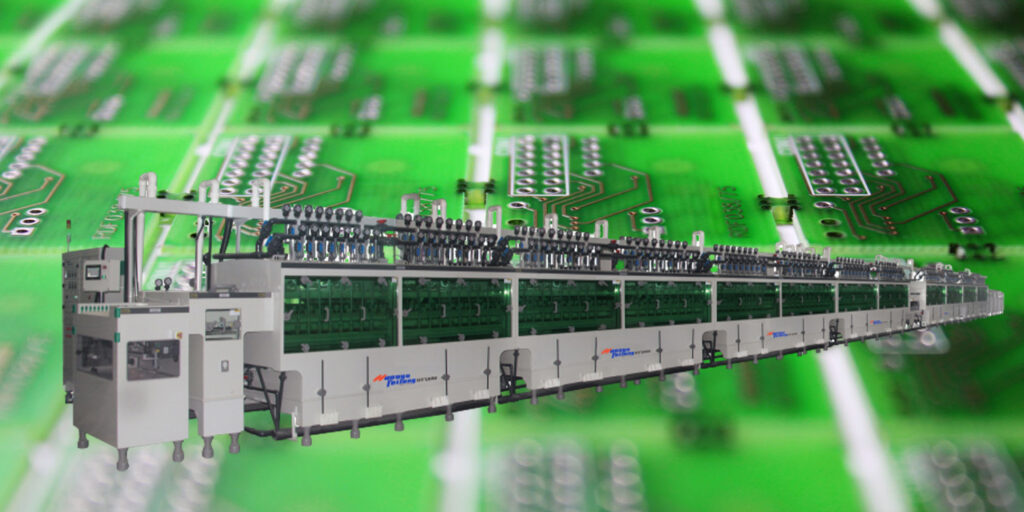
Chemical metal etching machines new
Learn about the metal etching process through video
4.2 Develop– Etch – Strip Line
The Develop – Etch – Strip Line is an essential part of the wet processing stage in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This line consists of three main processes: PCB development, PCB etching, and PCB stripping.
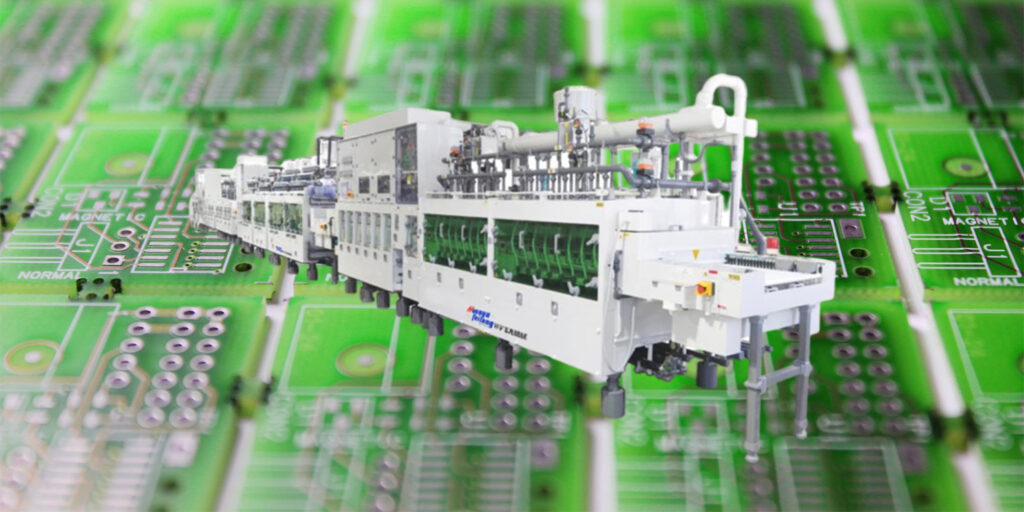
- PCB Development: The development process involves applying a photosensitive resist material onto the copper-clad PCB panel. This resist material is sensitive to light and helps protect certain areas of the copper surface from the subsequent etching process. The PCB panel is then exposed to UV light through a photomask that defines the circuit pattern. The UV light causes a chemical reaction in the resist material, resulting in the formation of a patterned photoresist layer. The unexposed resist material is then removed, revealing the underlying copper areas that will be etched.
- PCB Etching: Once the development process is complete, the PCB panel moves to the etching stage. Etching involves the removal of unwanted copper from the panel, leaving behind the desired circuit pattern. The panel is immersed in an etchant solution, usually an acidic solution such as ferric chloride or ammonium persulfate. The etchant selectively dissolves the exposed copper areas, while the patterned resist material acts as a barrier, protecting the copper traces and pads that form the circuit. This results in the creation of the circuit pattern on the PCB.
- PCB Stripping: After etching, the PCB panel still retains the patterned resist material. The purpose of the stripping process is to remove this resist material, leaving behind clean copper traces and pads. The panel is treated with a stripping solution that dissolves the resist material, typically an alkaline solution or a solvent. The resist material is dissolved and washed away, leaving only the copper circuitry on the PCB panel.
The Develop – Etch – Strip Line ensures precise and controlled removal of unwanted copper from the PCB, allowing the desired circuit pattern to be formed. Each step in the line plays a crucial role in the overall manufacturing process, with development defining the circuit pattern, etching removing excess copper, and stripping clearing away the resist material. This line is an integral part of PCB fabrication, ensuring the accurate creation of circuitry on the board.
Conclusion
By following this comprehensive guide, you can confidently choose the best etching machine for your specific production requirements. Revolutionize your PCB manufacturing process and unlock new levels of productivity, precision, and success.
